Introduction
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software plays a pivotal role in managing leads throughout their lifecycle—from initial collection to final conversion. Effective lead management ensures that businesses maximize opportunities, improve sales efficiency, and enhance customer relationships. This article explores the complete lead management process in CRM, covering lead collection, cleansing, nurturing, and conversion.
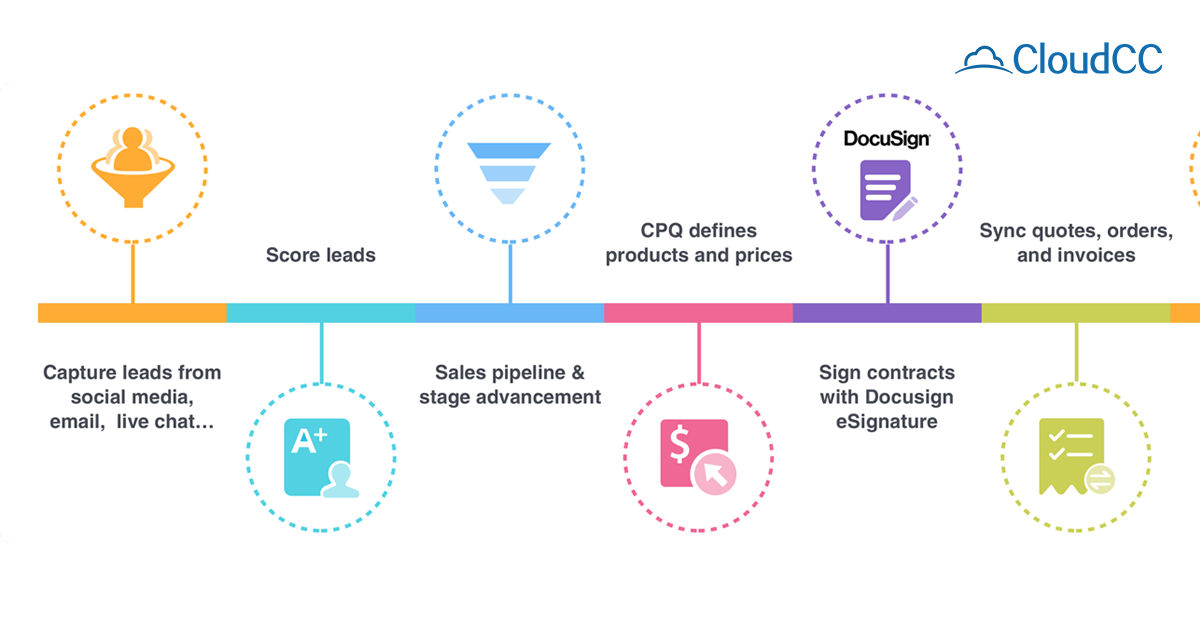
1. Lead Collection: Capturing Potential Customers
The first step in lead management is gathering potential customer data. CRM systems support multiple lead collection methods:
a. Web Forms & Landing Pages
Businesses capture leads via contact forms, subscription sign-ups, or gated content (e.g., whitepapers, e-books).
CRM integration with tools like HubSpot, Salesforce, or Marketo automates lead capture.
b. Social Media & Ads
LinkedIn, Facebook, and Google Ads generate leads, which can be imported into CRM systems.
CRM tools with ad tracking help attribute leads to specific campaigns.
c. Email & Cold Outreach
Sales teams collect leads from email campaigns, trade shows, or networking events.
CRM systems log interactions for follow-up.
d. Chatbots & Live Chat
AI-powered chatbots on websites engage visitors and collect lead information directly into the CRM.
2. Lead Cleansing: Ensuring Data Quality
Poor-quality data leads to wasted efforts. CRM systems help cleanse and standardize lead data through:
a. Deduplication
CRM tools identify and merge duplicate entries (e.g., same email with different names).
b. Validation & Enrichment
Email verification tools (e.g., ZeroBounce, Clearbit) check validity.
CRM integrations enrich profiles with job titles, company info, and social links.
c. Segmentation & Tagging
Leads are categorized by source, industry, behavior, or engagement level for targeted follow-up.
3. Lead Nurturing: Building Relationships
Not all leads are ready to buy immediately. CRM systems facilitate automated nurturing through:
a. Drip Email Campaigns
Personalized email sequences guide leads through the sales funnel.
CRM tools (e.g., Mailchimp, ActiveCampaign) track opens and clicks.
b. Behavioral Triggers
If a lead downloads an e-book or visits pricing pages, the CRM triggers follow-ups.
c. Lead Scoring
CRM assigns scores based on engagement (email opens, website visits, demo requests).
High-scoring leads are prioritized for sales outreach.
d. Multi-Channel Engagement
CRM integrates with social media, SMS, and retargeting ads to keep leads engaged.
4. Lead Conversion: Turning Prospects into Customers
The final stage focuses on converting nurtured leads into paying customers.
a. Sales Handoff
CRM automatically assigns high-intent leads to sales reps.
Tools like Salesforce Pardot or HubSpot Sales Hub streamline handoffs.
b. Personalized Demos & Proposals
Sales teams use CRM insights to tailor pitches based on lead behavior.
c. Closing & Post-Sale Follow-Up
CRM logs deal stages (proposal sent, contract signed).
Post-sale, the CRM shifts to customer success management (upselling, feedback collection).
Conclusion
A well-structured CRM lead management process—collection, cleansing, nurturing, and conversion—ensures no potential customer falls through the cracks. By leveraging automation, data enrichment, and multi-channel engagement, businesses can optimize lead conversion rates and drive sustainable growth.
Key Takeaways: ✔ Use CRM integrations for seamless lead capture. ✔ Cleanse data regularly to maintain accuracy. ✔ Nurture leads with personalized, automated campaigns. ✔ Convert high-scoring leads with targeted sales strategies.
By mastering end-to-end lead management, businesses can turn prospects into loyal customers efficiently.